Creating Google Cloud Functions With Kotlin
Serverless with Kotlin: Building and Deploying HTTP Functions on GCP
In May 2020, Google announced that Java 11 was coming to Google Cloud Functions.
Naturally, I thought, “Excellent, but can I write functions in other JVM-based languages like Kotlin?”
Thankfully, there is no such limitation. You can write your functions in any JVM language of your choosing.
The source code for this example can be found on GitHub:
https://github.com/mwhyte-dev/kotlin-google-cloud-function
Prerequisites
You’ll need some things to follow along with this example:
Java 11
Gradle
Access to GCP with a sample project created
gcloud installed and authenticated
The source code is cloned and imported into your IDE of choice
Main Function
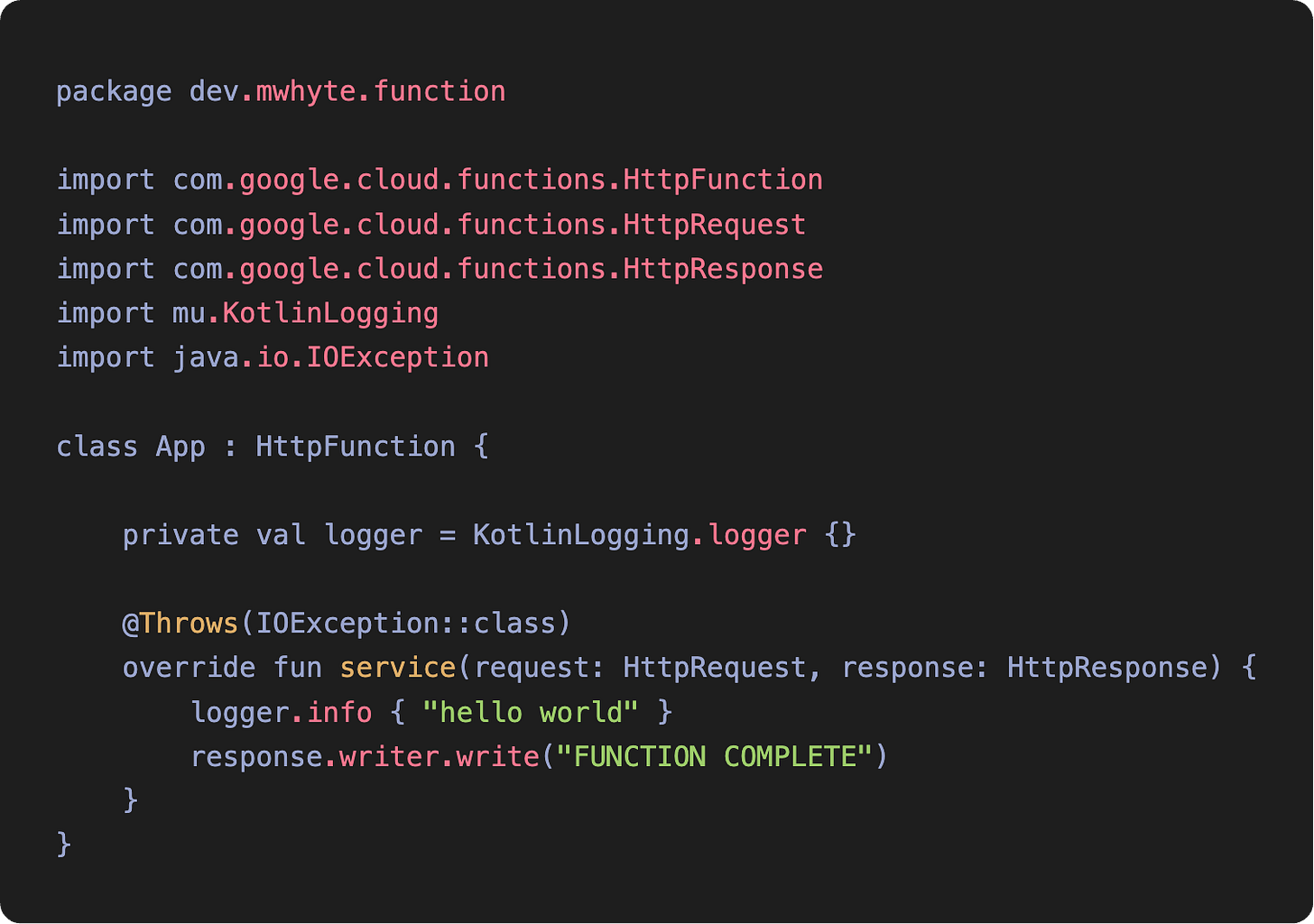
The main function is a straightforward one to get us started — a basic HTTP endpoint that will return the string “FUNCTION COMPLETE” when triggered:
This class extends HttpFunction from the functions-framework library. The service function takes an HttpRequest an HttpResponse object as parameters.
For non-HTTP ways to trigger a cloud function, you can use a RawBackgroundFunction or a typed variant.
For example: BackgroundFunction<PubSubMessage>
Some other options for triggering functions include Cloud Pub/Sub, Cloud Storage, Cloud Firestore, and various Firebase-based triggers.
You can find examples of other triggering mechanisms in the functions-framework-java readme.
Gradle Build File
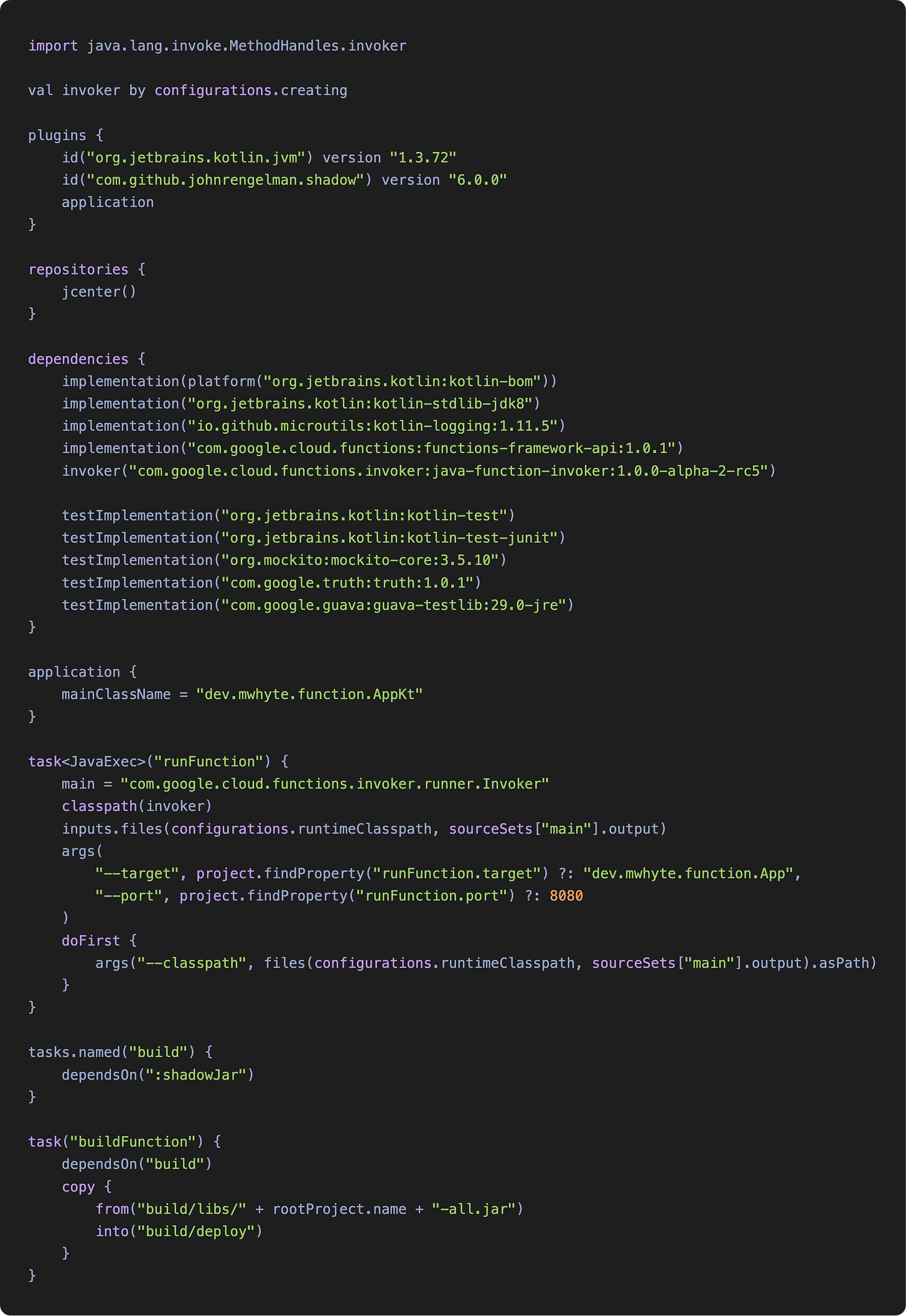
We use Gradle’s Kotlin DSL to configure our project for this example.
Dependencies
There are a few critical dependencies.
The Functions-framework-API allows us to write lightweight functions that run across many environments, including Google Cloud Functions and Cloud Run.
Java-function-invoker enables us to run the function locally for testing.
runFunction Task
The runFunction task in the Gradle build file triggers the java-function-invoker, which wraps the function and serves it using a Jetty web server.
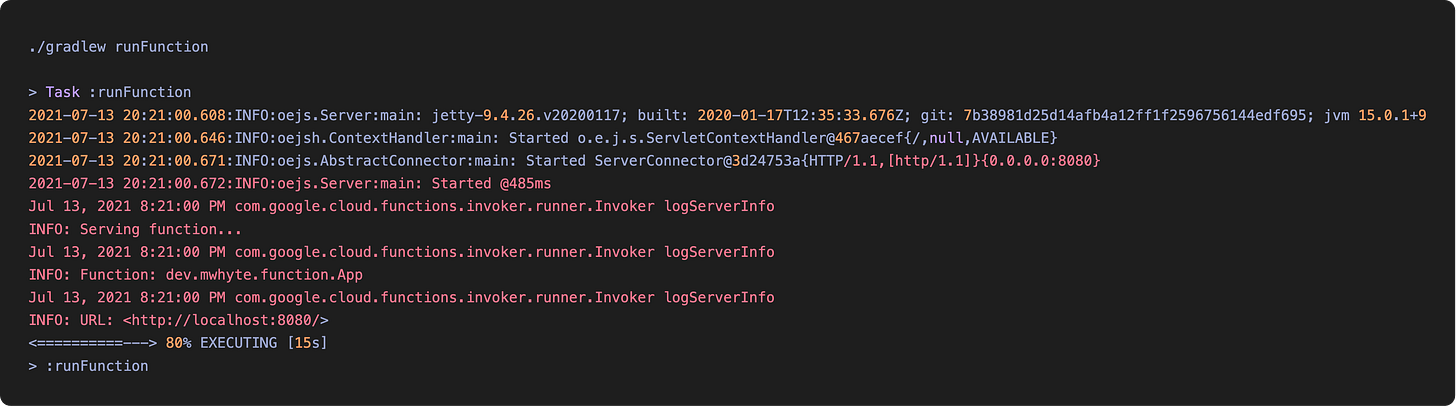
To run the function locally, call runFunction using the Gradle wrapper:
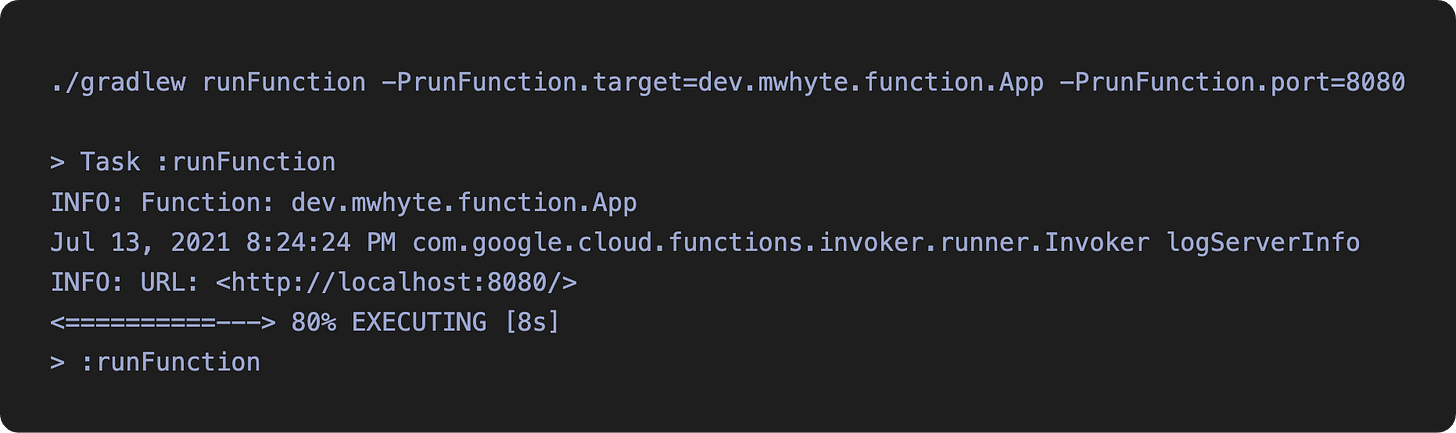
Optionally, you can override some args:
buildFunction Task
The buildFunction task in the Gradle build file works with the Gradle Shadow plugin to create a fat jar and copy it to the build/deploy directory. The jar is then ready to be uploaded to GCP Cloud Storage.
To execute this, use the Gradle wrapper:
Deploying with gcloud
So you’ve tested your function locally, built it, and now it's time to deploy. The gcloud command-line utility makes deployment easy.
First, ensure you are deploying to the GCP Project of your choice:
Then select the region you wish to deploy to :
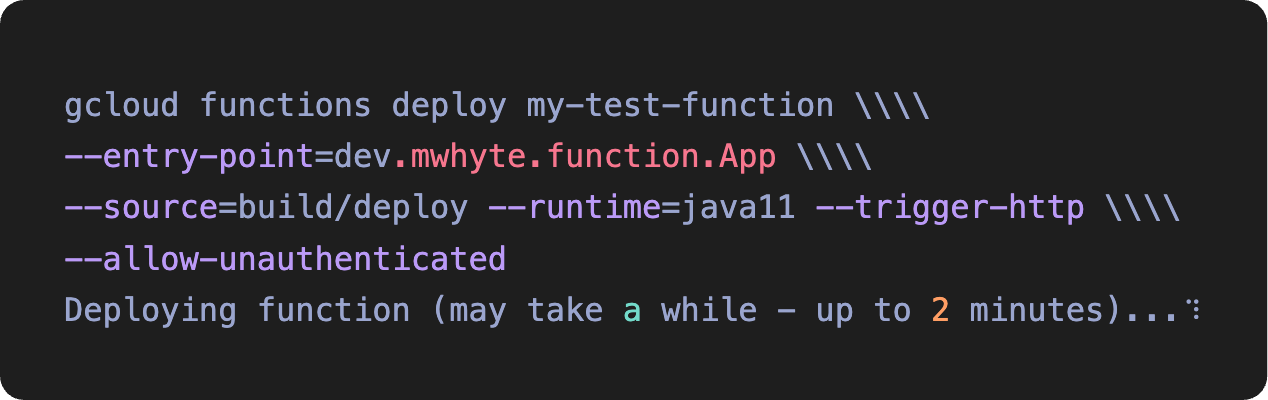
Lastly, deploy the function:
Note: The entry-point argument is the function's fully qualified class name, and the source is the location of our fat jar.
If you open the GCP console and navigate to Cloud Functions, you’ll see the function:
You can open it here and view various information, including the trigger. Alternatively, you can run a describe from gcloud:
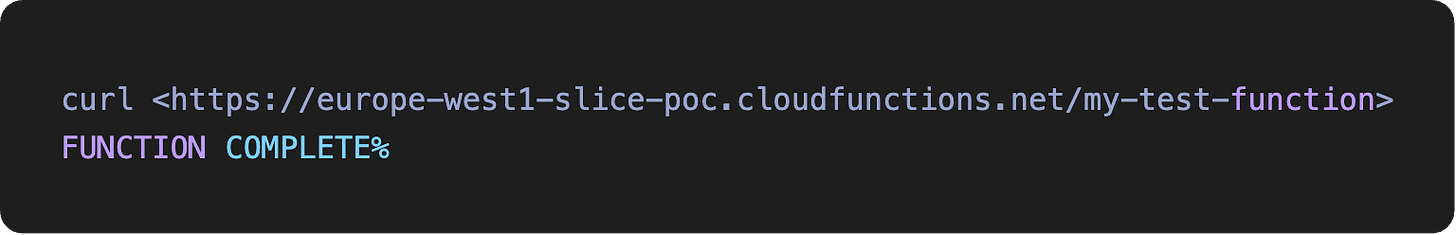
By hitting the trigger URL, you will see the function return the expected response:
References
We’ve seen how easy it is to deploy a Kotlin function to GCP. To explore the topic further, I’d recommend the following documentation:
https://github.com/mwhyte-dev/kotlin-google-cloud-function
Cloud Run functions documentation | Cloud Run functions Documentation | Google Cloud
https://github.com/GoogleCloudPlatform/functions-framework-java
https://github.com/GoogleCloudPlatform/functions-framework-java/issues/35